Enhanced fraud detection using ML and PySpark framework with feature selection
Introduction
Goal
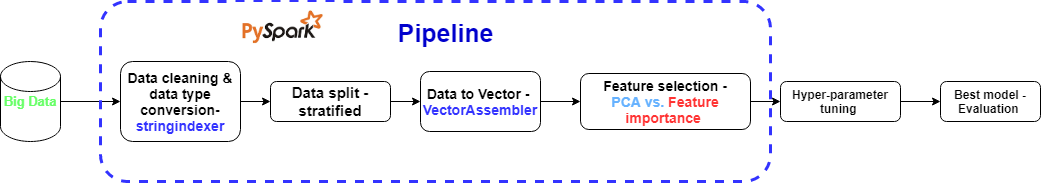
To examplify the feature selection strategy in PySpark and furhter enhanc the pyspark pipeline’s performance on fraud detection.
In this project, I will continue to work on the data from the project fradu_detection_ML_PySpark. The data exploration will be same, and the feature selction will use input perturbation strtegry instead of PCA as I did in the previous project.
Why feature selection?
1. Curse of dimensionality — Overfitting
The common theme of the problems is that when the dimensionality increases, the volume of the space increases so fast that the available data become sparse. This sparsity is problematic for any method that requires statistical significance.
In order to obtain a statistically sound and reliable result, the amount of data needed to support the result often grows exponentially with the dimensionality.
Also, organizing and searching data often relies on detecting areas where objects form groups with similar properties; in high dimensional data, however, all objects appear to be sparse and dissimilar in many ways, which prevents common data organization strategies from being efficient.
2. Occam’s Razor
We want our models to be simple and explainable. We lose explainability when we have a lot of features.
3 Noise in the data
In real applications, the data are not perfect and always noisy inherently.
Commonly used methods for feature selection
In summary, there are several commonly used methods to conduct feature selction in data preprocessing.
1 Correlation or chi-square
Chose the top-n high correlated variables or high chi-squre variables with respective to target variables. The intuition is that if a feature is independent to the target, it will not be useful or uninformative for target classification or regression.
2 Stepwise method
This is a wrapper based method. The goal of recursive feature elimination (RFE) is to select features by recursively considering smaller and smaller sets of features. First, the estimator is trained on the initial set of features and the importance of each feature is obtained either through a coef_ attribute or through a feature_importances_ attribute. Then, the least important features are pruned from current set of features. That procedure is recursively repeated on the pruned set until the desired number of features to select is eventually reached.
3 Lasso - Penalized likelihood
LASSO models have been used extensively in high-dimensional model selection problems, that is when the number of IVs 𝑘 by far exceeds the sample size 𝑛.
Regression coefficients estimated by the LASSO are biased by intention, but can have smaller mean squared error (MSE) than conventional estimates. It prefer to have fewer variales with huge contribution to the target.
Because of the bias, their interpretation in explanatory or descriptive models is difficult, and confidence intervals based on resampling procedures such as the percentile bootstrap do not reach their claimed nominal level. Another problem with LASSO estimation is its dependence on the scale of the covariates
4 PCA
PCA is a commonly used as dimension reduction technique by projecting each data point onto only the first few principal components to obtain lower-dimensional data while preserving as much of the data’s variation as possible.
The advantages of PCA:
- Removes Correlated Features
- Improves Algorithm Performance
- Reduces Overfitting
- Improves Visualization
The things we need to consider before using PCA:
- Independent variables become less interpretable:
- Data standardization is must before PCA: pca is affected by scale
- Information loss
5 Input Perturbation
This algorithm was introduced by Breiman in his seminal paper on random forests. Although he presented this algorithm in conjunction with random forests, it is model-independent and appropriate for any supervised learning model.
This algorithm, known as the input perturbation algorithm, works by evaluating a trained model’s accuracy with each of the inputs individually shuffled from a data set. Shuffling an input causes it to become useless—effectively removing it from the model. More important inputs will produce a less accurate score when they are removed by shuffling them. This process makes sense, because important features will contribute to the accuracy of the model.
Project link: https://github.com/tankwin08/Improved_fraud_detection_PySpark_feature_importances